Plasma
- FACTORS AFFECTING ION REACTION IN THE PLASMA -
RF Power
- Energy source for ionization to excite gas atoms
Why RF
- Ion particles are generally excited with electric fields, but pulsing is needed to compensate charge of ion to counter react before its charge decays.
- Excites ion more violently and radicals
Vacuum
- Vacuum creates an atmosphere to increase boiling point at low temperature
Reaction Gas
- Inert gas if excited in a Plasma invironment creates radical ion
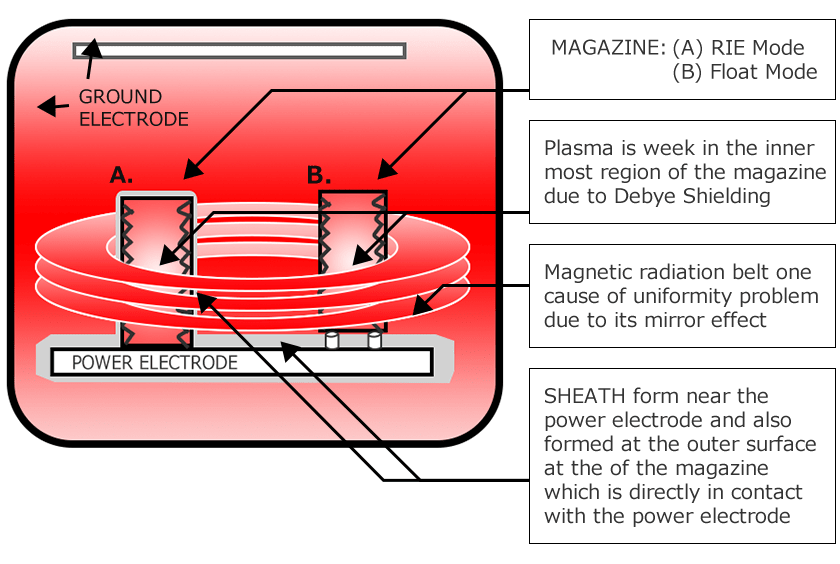
Sheath
- The region of strong electric field in front of material surface in contact with a plasma Its thickness is the Ion Sheath Length.
Debye Shield
- If a plate or metal may it be negative or positive charge is inserted into a plasma, it will change the local charge distribution by attracting or repelling electrons. The net result is an additional negative or positive charge density which cancles the effect of the initial charge at distances large compared to the debye length.
There is a corresponding effect of shielding by ions, which, for various and subtle reasons
Van Allen Belt
- The magnetic belt regions in which charged particles are trapped by the magnetic mirror effect.
Mirror Effect
- A charged particle travelling into an increasing magnetic field will reverse direction and be reflected back, provided its velocity perpendicular to to the field is sufficiently large relative to its parallel velocity. This magnetic mirror effect is a direct result of the adiabatic invariance of the magnetic moment. The mirror effect occurs in some plasmas, since the toroidal magnetic field is stronger on the inboard side than on the outboard side; in this case it gives rise to so-called " neoclassic" bahavior.
